Introduction
Hydrostatic testing is a method to determine strength, expose defects, expose leak & validate integrity of the vessel. Typically, tests are conducted at 125% of MAOP.
These tests are limited to defects that are ready for failure such as cracks. The test pressure must be adjusted for the related allowable stress at the design temperature. This requires adjustments during the testing phase due to ambient temperature conditions.
F_{wp} = \frac{1}{1 – \left(4.5 \times 10^{-5}\right) \left(\frac{P}{14.73}\right)}
F_{wp} = \frac{1}{1 - \left(4.5 \times 10^{-5}\right) \left(\frac{P}{14.73}\right)}
Where:
𝑃 − Test Pressure (psi
𝐹𝑤𝑝 − Water Compressibility due to Increase of Pressure
F_{pp} = \frac{1 + \left(\frac{D}{Wt}\right)(0.91P)}{ \left(30 \times 10^6\right) + \left(3.68 \times 10^{-6}\right)(T_1 – 60)}
F_{pp} = \frac{1 + \left(\frac{D}{Wt}\right)(0.91P)}{ \left(30 \times 10^6\right) + \left(3.68 \times 10^{-6}\right)(T_1 - 60)}𝐹𝑝𝑝 − Volume Change due to Increase of Pressure
𝐷 − Pipe Diameter (in)
𝑊𝑡 − Pipe Wall Thickness (in)
𝑃 − Test Pressure (psi)
𝑇1 − Test Temperature (°F)
F_{pt}=1+(18.2\times10^{-6})(T_1-60)
F_{pt}=1+(18.2\times10^{-6})(T_1-60)𝐹𝑝𝑡 −Volume Change due to Temperature Change
F_{pwt} = \frac{F_{pt}}{F_{wt}}
F_{pwt} = \frac{F_{pt}}{F_{wt}}𝐹𝑝𝑤𝑡 − Volume Change Ratio Pipe/Water
𝐹𝑤𝑡 − 𝑤𝑡 Factor Lookup Table
v=0.0408(D-2Wt)^2L
v=0.0408(D-2Wt)^2L
𝑣 − Pipe Fill Volume (gal)
𝐿 − Pipe Length (mi)
V_{tp}=vF_{wp}F_{pp}F_{pwt}
V_{tp}=vF_{wp}F_{pp}F_{pwt}𝑉𝑡𝑝 − Volume Required for Hydro Testing (gal)
𝑉𝑖 − Incremental Volume Required for Hydro Testing (gal)
V_i = V_{tp} – v \~\ t = \left(\frac{5}{9}\right)(T_1 + 40) – 40 \~\ Dp_1 = \frac{(B – 2A)}{\bigg(\frac{D(1 – ni^2)}{EWt} +{C_1}\bigg)} \quad Dp_2 = \frac{(B – 2A)}{\bigg(\frac{D(1 – ni^2)}{EWt} +{C_2}\bigg)} \~\ dp_1 = \frac{Dp_1}{\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)(1 + 40) – 40} \quad dp_2 = \frac{Dp_2}{\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)(1 + 40) – 40}
V_i = V_{tp} - v \\~\\ t = \left(\frac{5}{9}\right)(T_1 + 40) - 40 \\~\\ Dp_1 = \frac{(B - 2A)}{\bigg(\frac{D(1 - ni^2)}{EWt} +{C_1}\bigg)} \quad Dp_2 = \frac{(B - 2A)}{\bigg(\frac{D(1 - ni^2)}{EWt} +{C_2}\bigg)} \\~\\ dp_1 = \frac{Dp_1}{\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)(1 + 40) - 40} \quad dp_2 = \frac{Dp_2}{\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)(1 + 40) - 40}𝐶1 − Compressibility Factor for Water (3rd degree poly fit)(in3/in3/gal)
𝐶2 − Compressibility Factor for Water (5th degree poly fit)(in3/in3/gal)
𝑑𝑝1 − Pressure Change (3rd degree poly fit)(psi/℉)
𝑑𝑝2 − Pressure Change (5th degree poly fit)(psi/℉)
𝐸 − Modulus of Elasticity
𝑡 − Test Temperature (℉)
𝑛𝑖 − Poisson′s Ratio (ni = 0.3)
𝐴 − Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Pipe Material (1/℉)
Case Guide
Part 1: Create Case
- Select the Pipeline Hydrostatic Testing application from the Testing Module
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required Parameters.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button to overview results.
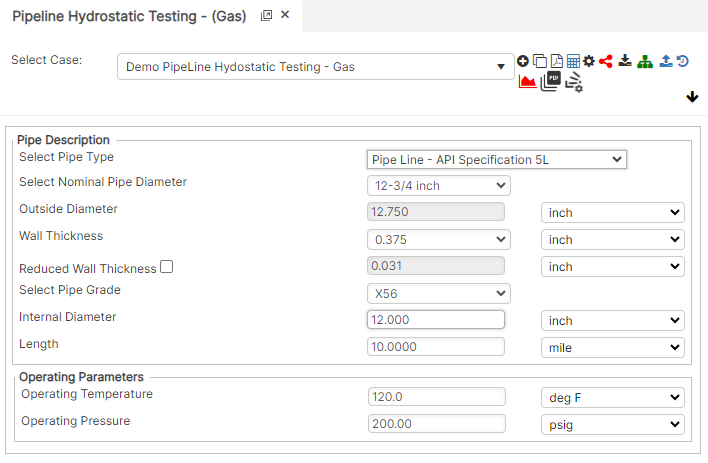
Input Parameters
- Nominal Pipe Size (in) : (0.625” – 48”)
- Outside Diameter (in)
- Wall Thickness (in) : (0.068”- >2”)
- Pipe Grade
- Internal Diameter (in)
- Pipeline Length (miles)
- Test Temperature (°F)
- Test Pressure (psig)
Part 2: Outputs/Reports
- If you need to modify an input parameter, click the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
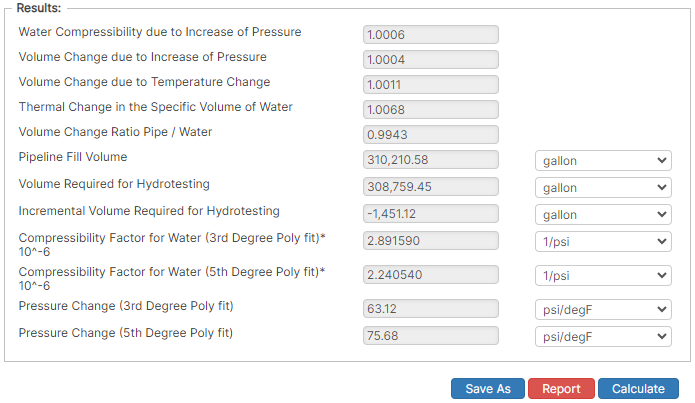
Results
- Water Compressibility due to Increase of Pressure
- Volume Change due to Increase of Pressure
- Volume Change due to Temperature Change
- Volume Change Ratio Pipe/Water
- Pipeline Fill Volume (gal)
- Volume Required for Hydrotesting (gal)
- Incremental Volume Required for Hydrotesting (gal)
- Compressibility Factor for Water (3rd Degree Poly fit) (in³/in³/psig) x10-6
- Compressibility Factor for Water (5th Degree Poly fit) (in³/in³/psig) x10-6
- Pressure Change (3rd Degree Poly fit) (psi/°F)
- Pressure Change (5th Degree Poly fit) (psi/°F).
References
- Pipeline Design for Hydrocarbons Gases and Liquids, Committee of pipeline planning, American Association of Civil Engineers, 1975
- Engineering Data Book, Volume II, Gas Processor Association, Revised Tenth Edition, 1994
- Pipeline Design & Construction, A Practical Approach, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2000
FAQ
-
Gas Purging Calculations?
Purging is a process of removing gas from the pipeline. Controlled purging of gases from pipelines by direct displacement with other gases that have been safely practiced for many years with the recognition that some flammable mixture is present. Purging of gases from pipelines by direct displacement with another gas also has been similarly practiced. It works both ways; however, there will always be an atmosphere of type of a mixture. This is due to the densities of the gases. Check Out
-
What are the differences between the Semiempirical Blowdown calculation and the AGA Blowdown calculation?
AGA blowdown calculation is based on the specification defined by American Gas Association. Semiempirical blowdown calculation was developed from the SW Research Report calculations for the blowdown time and mass of gas vented to atmosphere of a piping system. Check Out
