Maximum Impact Load & Penetration Depth
The focal point of this application is to assess strain due to a falling object such as a piece of construction equipment, material or vehicle falls over an operating pipeline.
Some of the limitations of this calculation are as follows: drop height, maximum load at the soil surface, type of soil, etc. to determine the penetration depth.
Maximum Impact Load
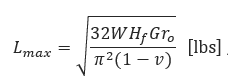
Where:
𝐿𝑚𝑎𝑥 − Maximum Load at Soil Surface(lbs)
𝑊 − Weight of Falling Object(lbs)
𝐻𝑓 − Drop Height(in)
𝑟𝑜 − Least Horizontal Radius of Falling Object(in)
𝐺 − Soil Shear Modulus(psi)
𝑣 − Poisson′s Ratio for Soil(dimensionless)
For large strains, near the region of impact, the shear modulus is one-tenth the low amplitude shear modulus.
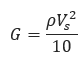
Where:
𝑉𝑠 − Shear Wave Velocity of Near Surface Soils(in/sec)
𝜌 − Mass Density of Near Surface Soil(Unit Weight of Soil/Acceleration due to Gravity)(lb.sec2/in4)
Penetration Depth
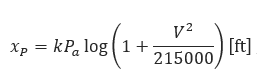
Where:
𝑥𝑝 − Penetration Depth(ft)
𝑃𝑎 −Weight per Unit Impact Area(lb/ft2)
𝑉 − Impact Velocity— ![]()
𝑘 − Empirical Coefficient of Penetration
(𝑘=0.0367 for Sandy Soil, k=0.0482 for Soil with Vegetation, k=0.0732 for Soft Soil)
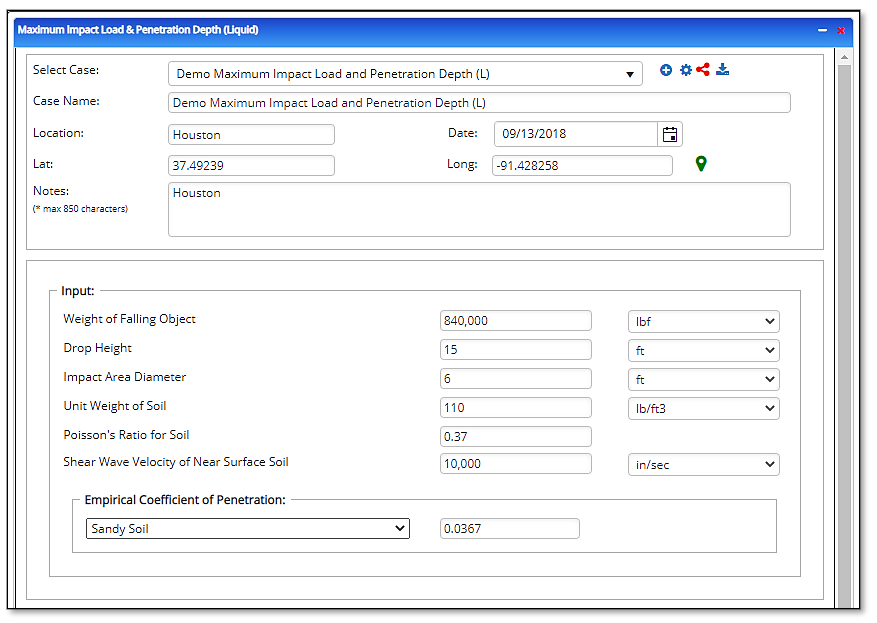
Input Parameters
- Select the Maximum Impact Load & Penetration Depth application from the Steel Pipe – Design and Stress Analysis module
- To create a new case, click the “+” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes
- Fill out all required fields
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units
- Click the CALCULATE button
- Weight of Falling Object(lbs.)
- Drop Height(ft), Impact Area Diameter(ft)
- Unit Weight of Soil(lbs./ft³)
- Poisson’s Ratio for Soil
Shear Wave Velocity of Near Surface Soil(in/sec) - Empirical Coefficient of Penetration
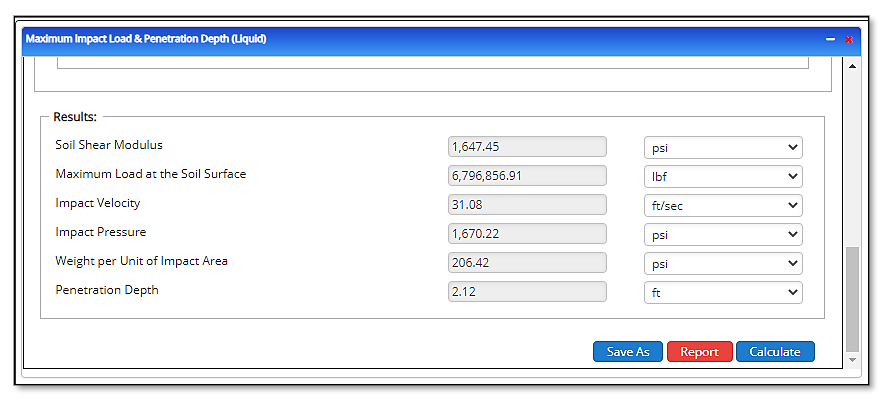
Outputs/Reports
- View the results
- If an input parameter needs to be edited be sure to hit the CALCULATE button after the change
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel/PowerPoint icon
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget
- Soil Shear Modulus(psi)
- Maximum Load at the Soil Surface(lbs.)
- Impact Velocity(ft/sec)
- Impact Pressure(psi)
- Weight per Unit of Impact Area(psi)
- Penetration Depth(ft)
Related Links
Pipeline Design & Stress Analysis
Pipeline HUB — User Resources
