Maximum Allowable and Minimum & Required Mud Pressure
Mud Management
Inadvertent returns of the drilling fluid to the surface are often a significant issue for HDD installations. Even though the drilling fluid is usually a non-toxic fluid containing mainly fresh water and 1% to 3% bentonite, accidental surface returns can be detrimental. The risk of inadvertent returns can be reduced by proper HDD design and good drilling practices.
Hydro-fracture occurs in non-fissured cohesive soils when the pressure gradient in the borehole exceeds the formation pressure gradient. This happens when the drilling fluid pressure exceeds the strength and confining stress of the surrounding soils. Under these conditions, the pressure fractures the soil around the borehole wall and allows the drilling fluid to escape the annulus. The likelihood of this occurring is often modeled with the cavity expansion model
The cavity expansion model can be used to calculate the estimated maximum allowable drilling fluid pressure in a borehole. The risk of hydrofracture can be evaluated by calculating the maximum allowable pressure with the following cavity expansion equation (often referred to as the Delft Equation). The minimum required pressure needs to be considerably lower than the maximum allowed pressure to reduce the chance of hydrofracture.
Initial Ground Water Pressure:
𝜇 = 𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 ∗ (ℎ𝑤)
𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 = Unit weight of water above the groundwater (lb/ft3)
ℎ𝑤 = Depth of the bore below groundwater elevation (ft)
Unit Weight of Soil Below Groundwater Elevation:
𝛾𝑤 = 𝛾𝑠𝑜𝑖𝑙 − 𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
γsoil = Unit weight of soil above the groundwater (lb/ft3)
Radius of Plastic Zone:
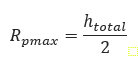
htotal = Depth of the bore below ground surface (ft)
Effective Stress:
𝜎0 = 𝛾𝑤 ∗ ℎ𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙
Maximum Allowable Mud Pressure:
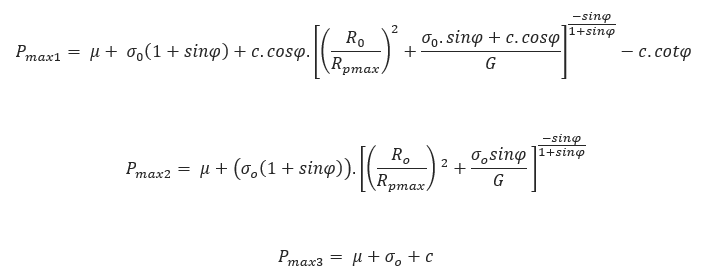
Φ = Soil friction angle (degree)
R0 = Borehole radius (inch)
C =Cohesion coefficient (lb/ft2)
G = Shear modulus of soil (lb/ft2)
Minimum Required Mud Pressure:
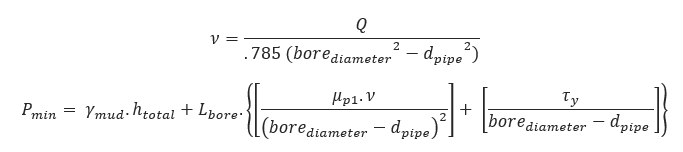
ϒmud = Unit weight of drilling fluid (lb/gal)
Lbore = Distance from the rig entry point (ft)
Borediameter = Borehole diameter (inch)
dpipe = Drill or pipe product outside diameter (inch)
µp1 = Viscosity of drilling fluid (cP)
τy = Yield point of drilling fluid (lb/100ft2
Input Parameters (Single Point)
- Borehole Diameter [inch]
- Drill or Pipe Product Outside Diameter [inch]
- Unit Weight of Drilling Fluid [lb/gal]
- Mud Flow Rate [gal/min]
- Yield Point of Drilling Fluid [lb/100ft2]
- Viscosity Drilling Fluid [cP]
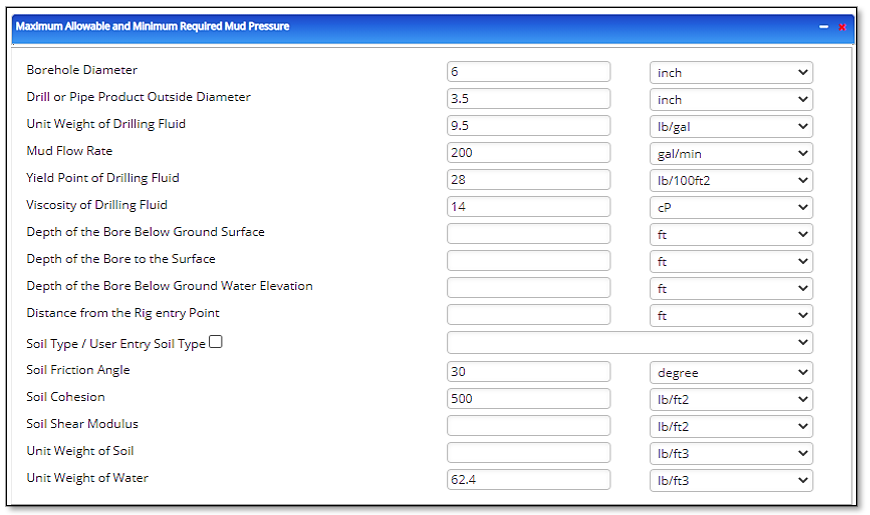
- Depth of the Bore below Ground Surface [ft]
- Depth of the Bore to the Surface [ft]
- Depth of the Bore below Groundwater Elevation [ft]
- Distance from the entry Point [ft]
- Soil Type
- Soil Friction Angle [degree]
- Soil Cohesion [lb/ft2]
- Soil Shear Modulus [lb/ft2]
- Unit Weight of Soil [lb/ft3]
- Unit Weight of Water [lb/ft3]
Outputs/Reports (Single Point)
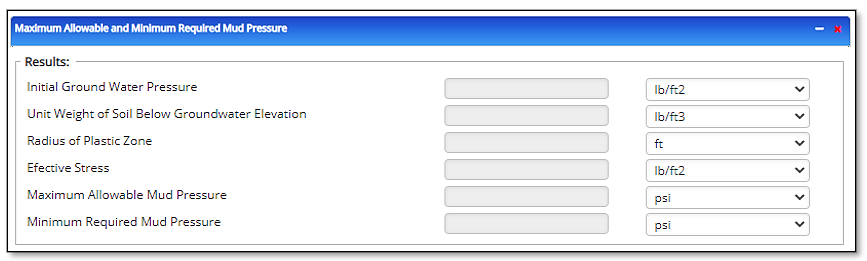
- Initial Ground Water Pressure [lb/ft2]
- Unit Weight of Soil Below Groundwater Elevation [ [lb/ft3]
- Radius of Plastic Zone [ft]
- Effective Stress [lb/ft2]
- Maximum Allowable Mud Pressure [psi]
- Minimum Allowable Mud Pressure (HDD Consortium) [psi]
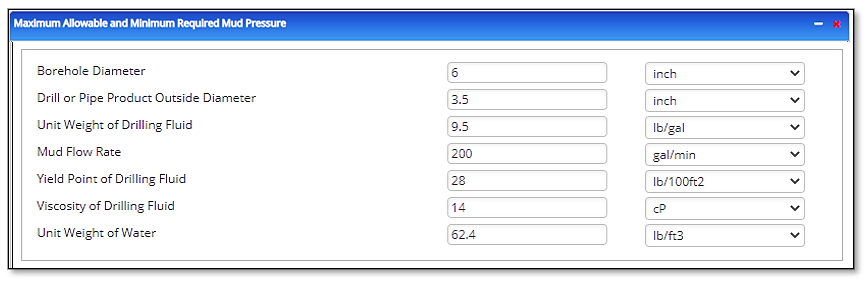
Input Parameters (Multiple Point)
- Borehole Diameter [inch]
- Drill or Pipe Product Outside Diameter [inch]
- Unit Weight of Drilling Fluid [lb/gal]
- Mud Flow Rate [gal/min]
- Yield Point of Drilling Fluid [lb/100ft2]
- Viscosity Drilling Fluid [cP]
- Unit Weight of Water [lb/ft3]
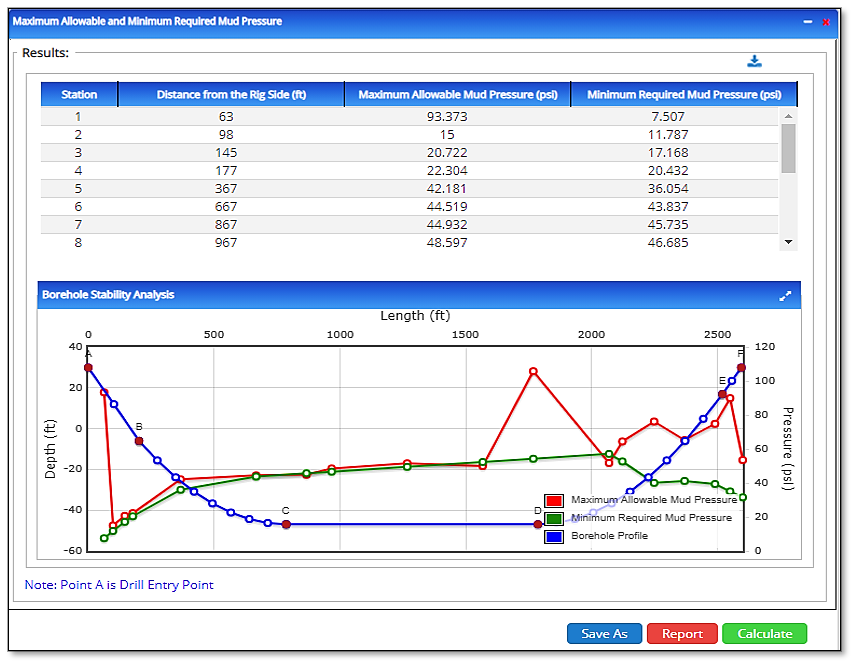
- Station
- Distance from the Rig Site
- Maximum Allowable Mud Pressure
- Minimum Required Mud Pressure
- Borehole Stability Analysis
- Plot/Graph
- Expanded Version
Outputs/Reports (Multiple Point)
Related Links
Horizontal Directional Drilling Hydraulic Fracture Analysis
