Introduction
This application uses a compression unit that calculates a natural gas-fired turbine to turn a centrifugal compressor. The centrifugal compressor is like a large fan inside a case, which pumps the gas as the fan turns.
Size of the fan and speed within the case controls the pumping action.
Adiabatic Compressor Horsepower:
HP = 0.0857 \left( \frac{k}{k – 1} \right) Q T_1z_{\text{avg}}\frac{1}{n_a} \left[ \left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} – 1 \right] \text{ in [HP]} \~\ or\~\HP = 0.0857 \left( \frac{k}{k – 1} \right) T_1z_{\text{avg}} \frac{1}{n_a} \left[\left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} – 1 \right] \text{ in [HP/MMSCFD]} \~\ z_{\text{avg}} = \frac{z_1 + z_2}{2} \~\ n_a = \left( \frac{T_1}{T_2 – T_1} \right) \left[ \left( \frac{z_1}{z_2} \right) \left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} – 1 \right]
HP = 0.0857 \left( \frac{k}{k - 1} \right) Q T_1z_{\text{avg}}\frac{1}{n_a} \left[ \left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} - 1 \right] \text{ in [HP]} \\~\\ or\\~\\HP = 0.0857 \left( \frac{k}{k - 1} \right) T_1z_{\text{avg}} \frac{1}{n_a} \left[\left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} - 1 \right] \text{ in [HP/MMSCFD]} \\~\\ z_{\text{avg}} = \frac{z_1 + z_2}{2} \\~\\ n_a = \left( \frac{T_1}{T_2 - T_1} \right) \left[ \left( \frac{z_1}{z_2} \right) \left( \frac{P_2}{P_1} \right)^{\frac{k-1}{k}} - 1 \right]
Where:
𝐻𝑃 − Adiabatic Compressor Horsepower
𝑄 − Gas Flow Rate (MMSCFD)
𝑇1−Suction Temperature (°𝑅)
𝑇2 − Discharge Temperature (°𝑅)
𝑧1 − Compressibility of Gas at Suction Conditions
𝑧2 − Compressibility of Gas at Discharge Conditions
𝑧𝑎𝑣𝑔 − Average Compressibility Factor
𝑘 = (𝑐𝑝/𝑐𝑣) − Specific Heat Ratio
𝑛𝑎 − Compressor Adiabatic (Isentropic) Efficiency
𝑃1 − Gas Suction Pressure (psia)
𝑃2 − Gas Discharge Pressure (psia)
CNGA/GPSA Compressibility Factor Approximation:
Z=\frac{1}{\left[1+\left(\frac{3.444\times10^5P\times10^{1.785G}}{T_f^{3.825}} \right)\right]}
Z=\frac{1}{\left[1+\left(\frac{3.444\times10^5P\times10^{1.785G}}{T_f^{3.825}} \right)\right]}Where:
𝑍 − Compressibility Factor
𝑃 − Pressure
𝑇𝑓 − Gas Flowing Temperature (°𝑅)
Brake Horsepower
BHP=\frac{HP}{n_m}
BHP=\frac{HP}{n_m}Where:
𝑛𝑚 − Mechanical Efficiency 𝑛𝑚 = 0.95/0.98
Case Guide
Part 1: Create Case
- Select the Required Adiabatic Horsepower application from the Compressor Module
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required Parameters.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button to overview results.
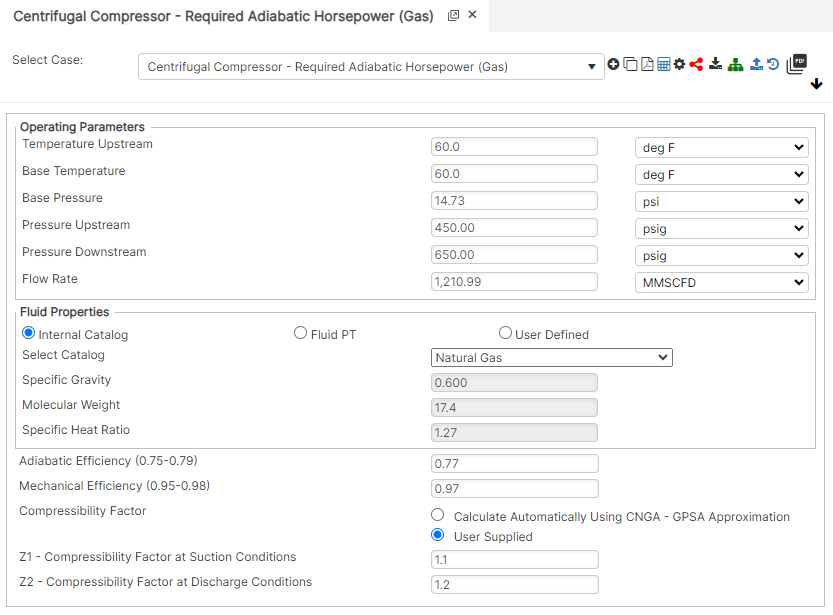
Input Parameters
- Suction Temperature Upstream (°F)
- Base Temperature (°F)
- Base Pressure (psi)
- Suction Pressure Upstream (psig)
- Discharge Pressure Downstream (psig)
- Capacity/Required Flow Rate (MMSCFD)
- Gas Specific Gravity (Relative to air)
- Gas Molecular Weight
- Gas Specific Heat Ratio
- Adiabatic Efficiency (0.75 – 0.79)
- Mechanical Efficiency (0.95 – 0.98)
- Z1 – Compressibility Factor at Suction Conditions
- Z2 – Compressibility Factor at Discharge Conditions
Part 2: Outputs/Reports
- If you need to modify an input parameter, click the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
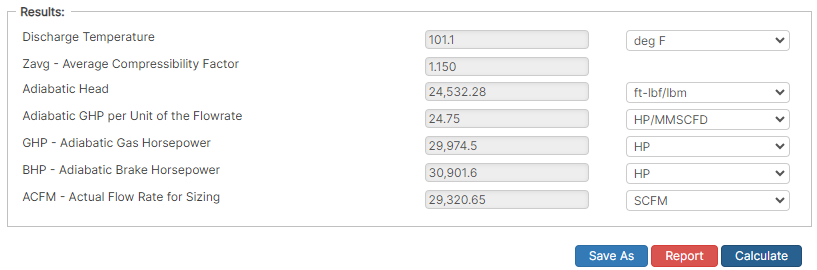
Results
- Discharge Temperature (°F)
- Zavg – Average Compressibility Factor
- Adiabatic Head (ft lbf/lbm)
- Adiabatic GHP per Unit of the Flowrate (HP/MMSCFD)
- GHP – Adiabatic Gas Horsepower (HP)
- BHP – Adiabatic Brake Horsepower (HP)
- ACFM – Actual Flow Rate for Sizing (ft³/min)
References
- Engineering Data Book, Volume 1, Gas Processors Suppliers Association, Tenth Edition
- Compressor Station Operation, Book T-2, GEOP, American Gas Association (A.G.A.)
- Compressor Selection and Sizing, Royce N. Brown, Second Edition, Gulf Professional Publishing
