Introduction
The average flow rate of [gasses/liquids] undergoing steady-state, isothermal purging can be represented using the Weymouth equation:
Q = 0.0181 \left(\frac{T_0}{P_{0}}\right)D^{2.666} \sqrt{\frac{P_1^2 – P_2^2}{G T Z L}} = 0.0361D^{2.666} \sqrt{\frac{P_1^2 – P_2^2}{L}) }= C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 – P_2^2}
Q = 0.0181 \left(\frac{T_0}{P_{0}}\right)D^{2.666} \sqrt{\frac{P_1^2 - P_2^2}{G T Z L}} = 0.0361D^{2.666} \sqrt{\frac{P_1^2 - P_2^2}{L}) }= C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - P_2^2}
Where:
𝑄 – Quantity of gas flowing [Mscf/h]
𝑃1 − Purge Gas Injection Pressure [psia]
P2 – Blowoff pressure (18-20 [psia])
L – Length of gas line [miles]
D – Internal pipe diameter [in]
T0 – Base measurement temperature (60 F = 520 R)
P0 – Base measurement pressure (14.73 lb/in^2 absolute)
G – Specific gravity of natural gas (0.6)
T – Mean flow temperature (60 F = 520 R)
C1 –
\frac{0.0361D^{2.666}}{\sqrt L}, \text{ where } D \text{ is in inch } \&\, L \text{ is in miles}
\frac{0.0361D^{2.666}}{\sqrt L}, \text{ where } D \text{ is in inch } \&\, L \text{ is in miles}
The blowoff pressure P2 should be kept between 18-20 psig and maintained. Assuming critical velocity at the blowout valve:
Q=KP_2=KP_1\sqrt{\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2+K^2}}
Q=KP_2=KP_1\sqrt{\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2+K^2}}Where:
K – Blowoff valve coefficient [Mscf/(h*psia)]
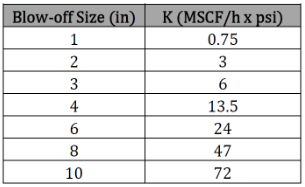
The average pressure of a pressurized pipeline is given as:
P_{ave}=P_1+P_2-\frac{P_1P_2}{P_1+P_2}
P_{ave}=P_1+P_2-\frac{P_1P_2}{P_1+P_2}The minimum time required to purge the pipeline (in hours) is given in Method A as:
t_m = \frac{\pi L D^2}{Q}\frac{ P_{ave}}{P_0} = \frac{(0.177) D^2 L P_{ave}}{C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 – P_2^2}}
t_m = \frac{\pi L D^2}{Q}\frac{ P_{ave}}{P_0} = \frac{(0.177) D^2 L P_{ave}}{C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - P_2^2}}
Which is algebraically equivalent to Method B:
T_m = (0.078) D^2 L \frac{1+ \frac{\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2K^2}}{1+\sqrt{ \frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2K^2} }}} {C_1 \sqrt{1-\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2+K^2}}}
T_m = (0.078) D^2 L \frac{1+ \frac{\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2K^2}}{1+\sqrt{ \frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2K^2} }}} {C_1 \sqrt{1-\frac{C_1^2}{C_1^2+K^2}}}
Where:
tm– minimum purge time [h]
It is recommended to purge the pipeline for twice the minimum purge time calculated above, for conservation’s sake.
trec=2tm
The total volume of natural gas lost in the purging (in Mscf) is given by:
V_{loss} = Q t – V_0 =\bigg( C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 – \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2}{C_1^2 – K^2}} \times \frac{t}{60} \bigg) – V_0
V_{loss} = Q t - V_0 =\bigg( C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2}{C_1^2 - K^2}} \times \frac{t}{60} \bigg) - V_0
V0 – The original volume of (assumed) air purged from the pipe [Mscf]
t – Purge time [min]
Method A
Recommended purge time is 2T. The minimum purge time in minute is
T_a = \left( \frac{0.117 (D^2) L P_M \sqrt{L}}{0.0361 D^{2.667} \sqrt{P_1^2 – P_2^2}} \right)
T_a = \left( \frac{0.117 (D^2) L P_M \sqrt{L}}{0.0361 D^{2.667} \sqrt{P_1^2 - P_2^2}} \right)
𝑇𝑎 − Minimum Purge Time (min)
𝑇𝑟𝑎 − Recommended Minimum Purge Time (min)
𝐶1 = 0.0361𝐷2.667/√𝐿
C_1 = \frac{0.0361 D^{2.667}}{\sqrt{L}}\~\V_a = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 – \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1 \~\ V_{ra} = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 – \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{2T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1
C_1 = \frac{0.0361 D^{2.667}}{\sqrt{L}}\\~\\V_a = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1 \\~\\ V_{ra} = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{2T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1
𝑉𝑎 − Volume of Gas Lost − (min) time (MSCF)
𝑉1 − Actual Volume of Pipe Section − Assume filled with air before purge (MCF)
𝑉𝑟𝑎 − Volume of Gas Lost − Recommended time (MSCF)
Method B
Recommended purge time is 2T. The minimum purge time in minute is
T_b = 0.0078 D^2 L \frac{1+ \frac{\frac{C_1^2}{K^2+C_1^2}}{1+\sqrt{ \frac{C_1^2}{K^2+C_1^2} }}} {C_1 + \sqrt{\frac{C_1^2}{K^2 + C_1^2}}}
T_b = 0.0078 D^2 L \frac{1+ \frac{\frac{C_1^2}{K^2+C_1^2}}{1+\sqrt{ \frac{C_1^2}{K^2+C_1^2} }}} {C_1 + \sqrt{\frac{C_1^2}{K^2 + C_1^2}}}
𝑇𝑏 − Minimum Purge Time (min)
𝑇𝑟𝑏 − Recommended Minimum Purge Time (min)
𝐶1 = 0.0361𝐷2.667/√𝐿
C_1 = \frac{0.0361 D^{2.667}}{\sqrt{L}}\~\V_b = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{p_1^2 – \frac{C_1^2 p_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1 \~\ V_{rb} = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{p_1^2 – \frac{C_1^2 p_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{2T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1
C_1 = \frac{0.0361 D^{2.667}}{\sqrt{L}}\\~\\V_b = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1 \\~\\ V_{rb} = \bigg(C_1 \sqrt{P_1^2 - \frac{C_1^2 P_1^2 }{K^2 + C_1^2}} \left(\frac{2T}{60}\right) \bigg)- V_1
𝑉𝑏 − Volume of Gas Lost − (min) time (MSCF)
𝑉1 − Actual Volume of Pipe Section − Assume filled with air before purge (MCF)
𝑉𝑟𝑏 − Volume of Gas Lost − Recommended time (MSCF)
Case Guide
Part 1: Create Case
- Select the Purging Calculations application from the Testing Module
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required Parameters.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button to overview results.
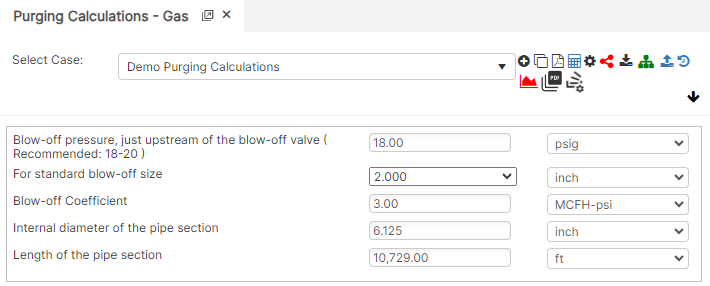
Input Parameters
- Blow-off Pressure, just Upstream of the Blow-off Valve (Recommended 18-20) (psig)
- For standard blow-off size (in) (dropdown)
- Blow-off Coefficient (MCFH-psi)
- Internal Diameter of Pipe Section (in)
- Length of Pipe Section (ft) (dropdown)
Part 2: Outputs/Reports
- If you need to modify an input parameter, click the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
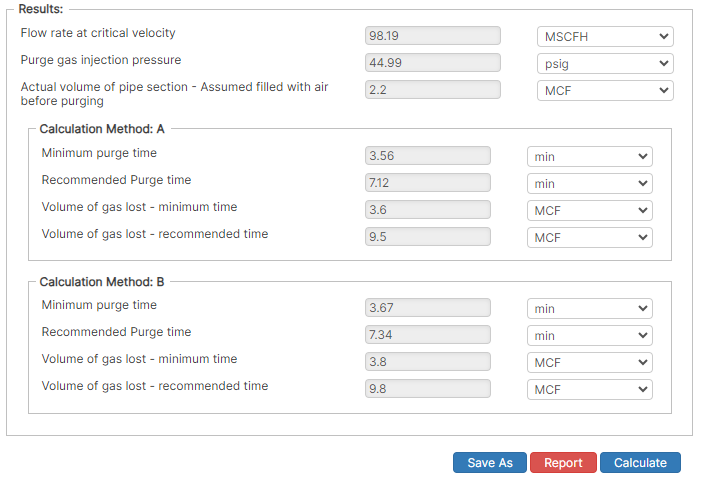
Results
- Flowrate at Critical Velocity (MSCF)
- Purge Gas Injection Pressure (psig)
- Actual Volume of Pipe Section (Assume filled with air before purging) (MCF)
- Calculation Method A/B
- Minimum Purge Time (min)
- Recommended Purge Time (min)
- Volume of Gas Lost – Minimum Time (MCF)
- Volume of Gas Lost – Recommended Time (MCF)
References
- Pipeline Design for Hydrocarbons Gases and Liquids, Committee of pipeline planning, American Association of Civil Engineers, 1975
- Engineering Data Book, Volume II, Gas Processor Association, Revised Tenth Edition, 1994
- Pipeline Design & Construction, A Practical Approach, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2000
FAQ
-
Gas Purging Calculations?
Purging is a process of removing gas from the pipeline. Controlled purging of gases from pipelines by direct displacement with other gases that have been safely practiced for many years with the recognition that some flammable mixture is present. Purging of gases from pipelines by direct displacement with another gas also has been similarly practiced. It works both ways; however, there will always be an atmosphere of type of a mixture. This is due to the densities of the gases. Check Out
-
What are the differences between the Semiempirical Blowdown calculation and the AGA Blowdown calculation?
AGA blowdown calculation is based on the specification defined by American Gas Association. Semiempirical blowdown calculation was developed from the SW Research Report calculations for the blowdown time and mass of gas vented to atmosphere of a piping system. Check Out
