Introduction
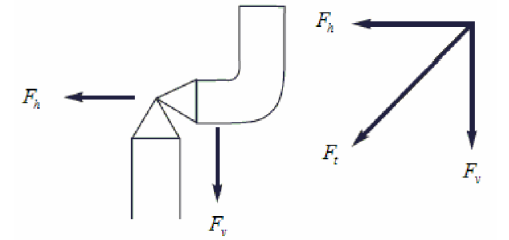
Where:
𝐹ℎ − Force due to Change in Momentum (lbs)
𝐹𝑣 − Force due to Discharge (lbs)
𝐹𝑡 = 𝑆𝐺∙𝑄/2722∙𝐴 Reactive Force (lbs)
𝑆𝐺 − Liquid Specific Gravity
Q − Flowrate (gal/min) 𝐴−Area of Outlet Pipe (in2)
P − Static pressure within the outlet at the pint of discharge(psig)
Case Guide
Part 1: Create Case
- Select the Relief Valve: Reactive Force application in the Facilities Module
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required parameters.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button to overview results.
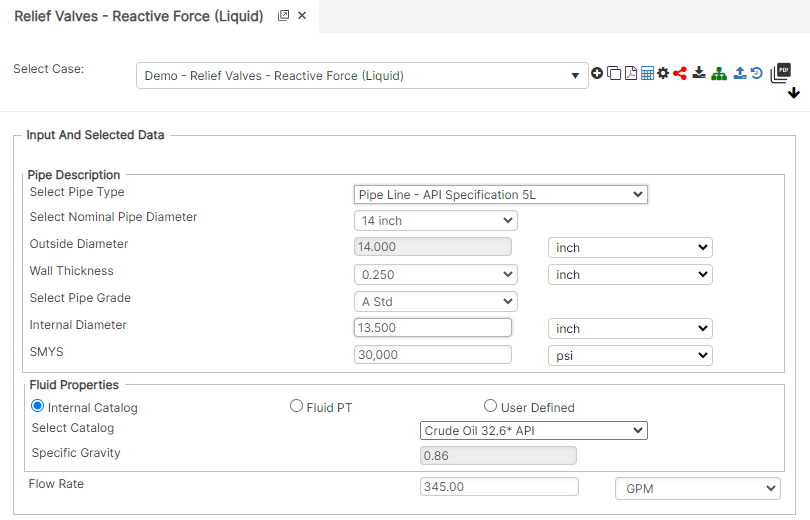
Input Parameters
- Pipe Type
- Pipe Outside Diameter (in)
- Pipe Wall Thickness (in)
- Internal Pipe Diameter (in)
- Specific Gravity Relative to H20 60°F/60°F
- Flow Rate (gal/min)
Part 2: Outputs/Reports
- If you need to modify an input parameter, click the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
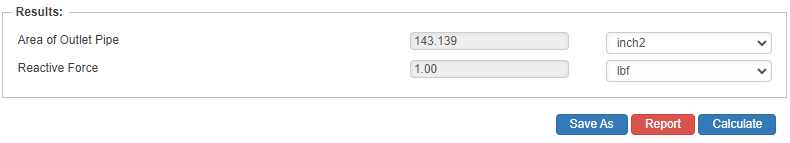
Results
- Area of Outlet Pipe (in2)
- Reactive Force (lbs)
References
- ASME – Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII
- API – RP 520 Part 2
- ASME B31.8 Gas Transmission and Distribution Piping Systems
- ASME B31.3, B31.4 and B31.8 – Full Encirclement Sleeves (See Appendices)
Appendix
Even though Technical Toolboxes does not provide software for a full-encirclement reinforcing saddles, many operators use them to provide reinforcement for branch outlets in accordance with ASME B31.3, B31.4, B31.8 and other applicable design codes. Full-encirclement reinforcing saddles are designed to fully encircle the run pipe however; they are not designed to be pressure retaining devices. To avoid gas entrapment during welding and to prevent pressure containment, should a leak develop underneath the saddles; these saddles should be provided with a vent to allow escaping product.
A typical field applied Full Encirclement Reinforcement Weldment Saddle is shown below:


FAQ
-
Validation check: Reinforcement of Welded Branch Connection?
This table highlights the list of validation checks that are in effect in the PLTB Gas > Pipeline Facilities> Reinforcement of Welded Branch Connection – ASME B31.8 calculation. Check Out
-
Orifice Coefficient for Hot Tap Sizing?
When a compressible fluid, such as natural gas or air, is passed through an orifice, the rate of flow is determined by the area of the orifice opening; the absolute upstream pressure is 𝑃1; and the absolute downstream pressure is 𝑃2: unless the ratio 𝑃2/𝑃1. equals or is less than the critical ratio. When 𝑃2/𝑃1 equals or is less than the critical ratio downstream pressure no longer effects rate of flow through the orifice, and flow velocity at the vene contracta is equal to the speed of sound in that fluid under that set of condition. This is commonly referred to as critical or sonic flow. Orifice equations are therefore classified as “sonic” or “subsonic” equations. Check Out
-
How is Required Area calculated for Branched Weld Connection?
The calculation is using the following is the equation that we use for A3 – REQUIRED AREA
A3 = Ar – A1-A’2
where:
Ar = Reinforcement Required
A1= Reinforcement Provided
A’2 = Corrected Effective Area
