AGA Fully Turbulent Flow
This is one of the most recommended and used equations for this type of flow, being able to estimate with high precision flow and pressure drop values if pipe roughness is known with correctness. It has been used for comparison among the different flow equations as a reference basis because it is fundamental to the definition of the corresponding application ranges and errors.
Similar to the Colebrook Equation, the AGA Equation uses a slightly modified transmission factor in order to obtain a value for the pressure drop using the General Flow Equation. The transmission value for the AGA equation is the following:
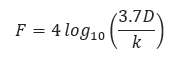
This equation is also known as the Von Karman equation for rough pipe flow.
𝐹 − Transmission Factor
𝑘 − Pipe Roughness
𝐷 − Internal Diameter (in)
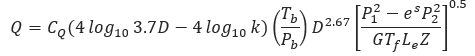
𝑄 − Flow Rate (FT3/day)
𝐶𝑄 − 38.774
𝑇𝑏 −Temperature Base (°R)
𝑃𝑏 − Pressure Base (psi)
𝑇𝑓 − Gas Flowing Temperature (°R)
𝐷 − Internal Diameter (in)
𝑘 − Pipe Roughness
𝑃1 − Upstream Pressure (psi)
𝑃2 − Downstream Pressure (psi)
𝐺 − Gas Specific Gravity
𝑍 − Compressibility Factor
Le − Pipe Segment Length including Expansion (mi)
𝑇𝑓 − Gas Flowing Temperature (°R)
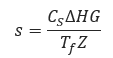
𝑠 − Elevation adjustment parameter
CS − 0.0375
𝑍 − Compressibility Factor
𝑇𝑓 − Gas Flowing Temperature (°R)
∆𝐻𝐺 − Change in Elevation (ft)
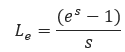
𝐿𝑒 − Pipe Segment Length including Expansion (mi)
𝑠 − Elevation adjustment parameter
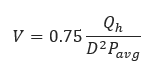
𝑉 − Velocity (ft/sec)
𝑄ℎ − Volumetric flow rate (scf/hr)
𝐷 − Internal Diameter (in)
𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑔 − Average Pipeline Pressure (psia)
𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐦𝐚𝐥𝐥 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐩 𝑷𝟐 > 𝟎.𝟖𝑷𝟏:
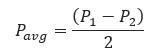
𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐠𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐩:
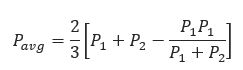
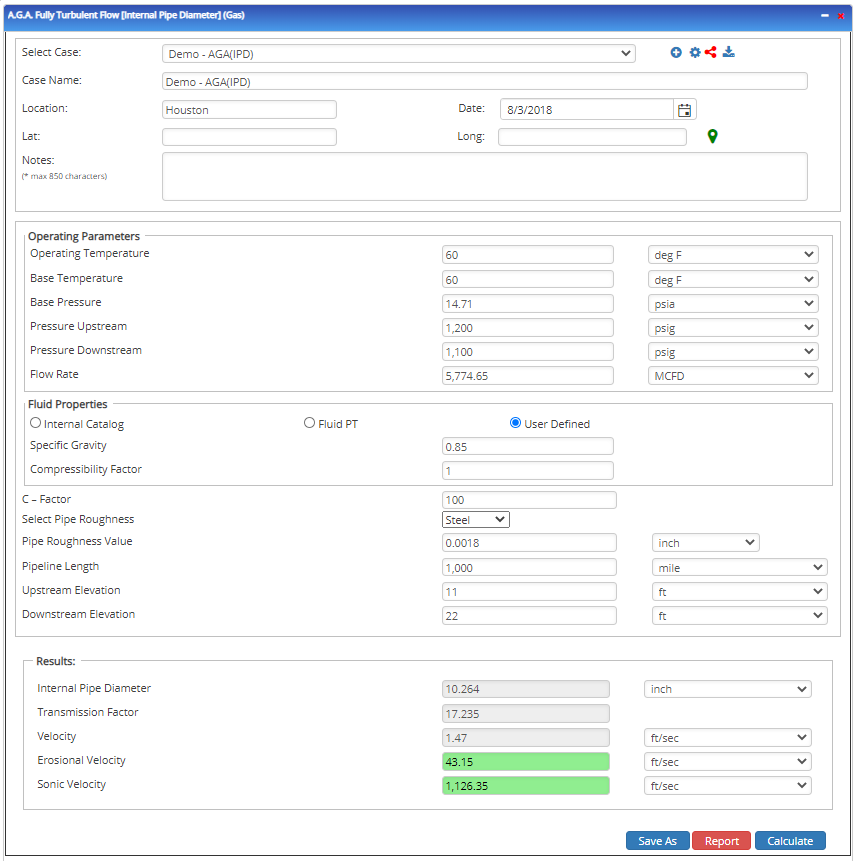
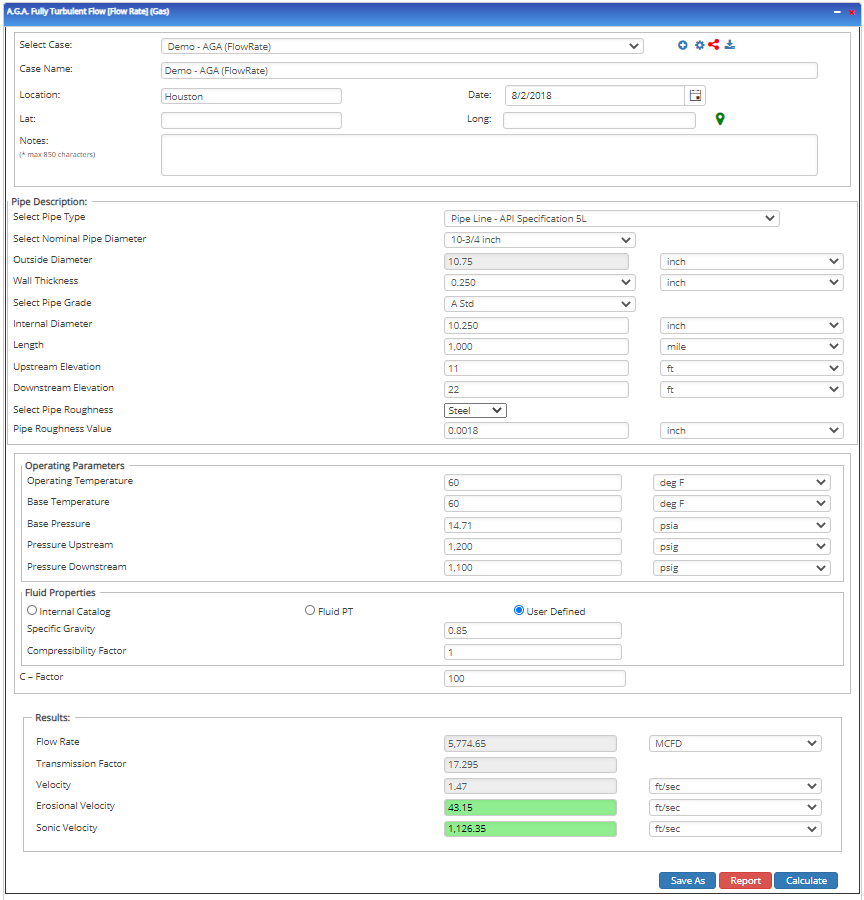
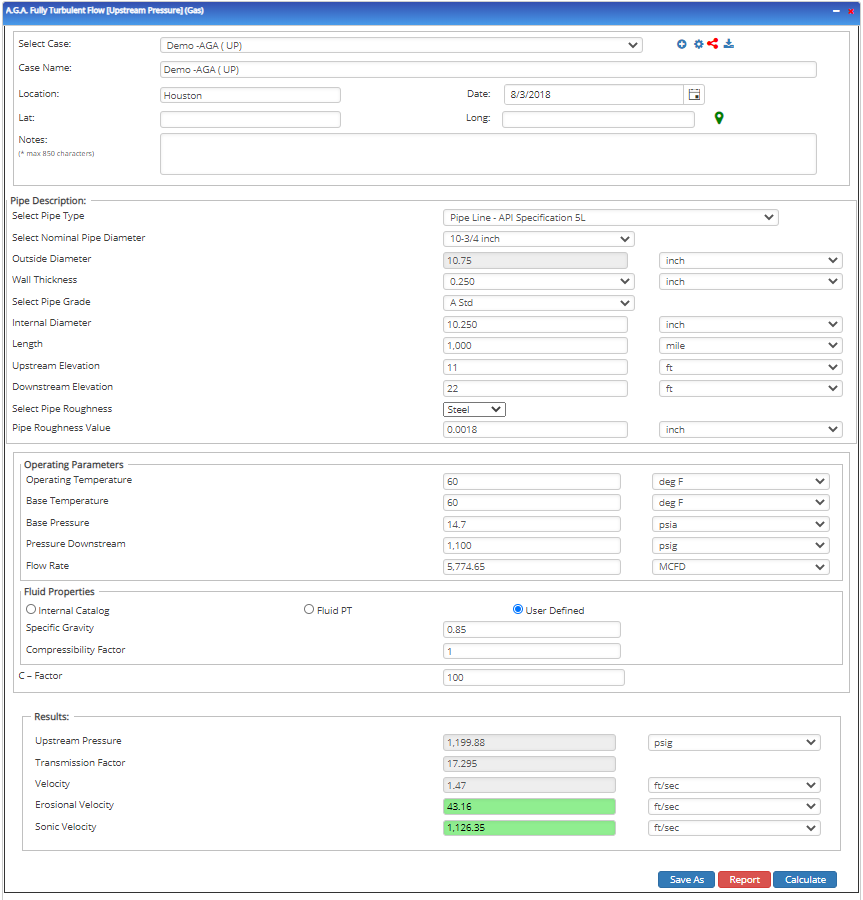
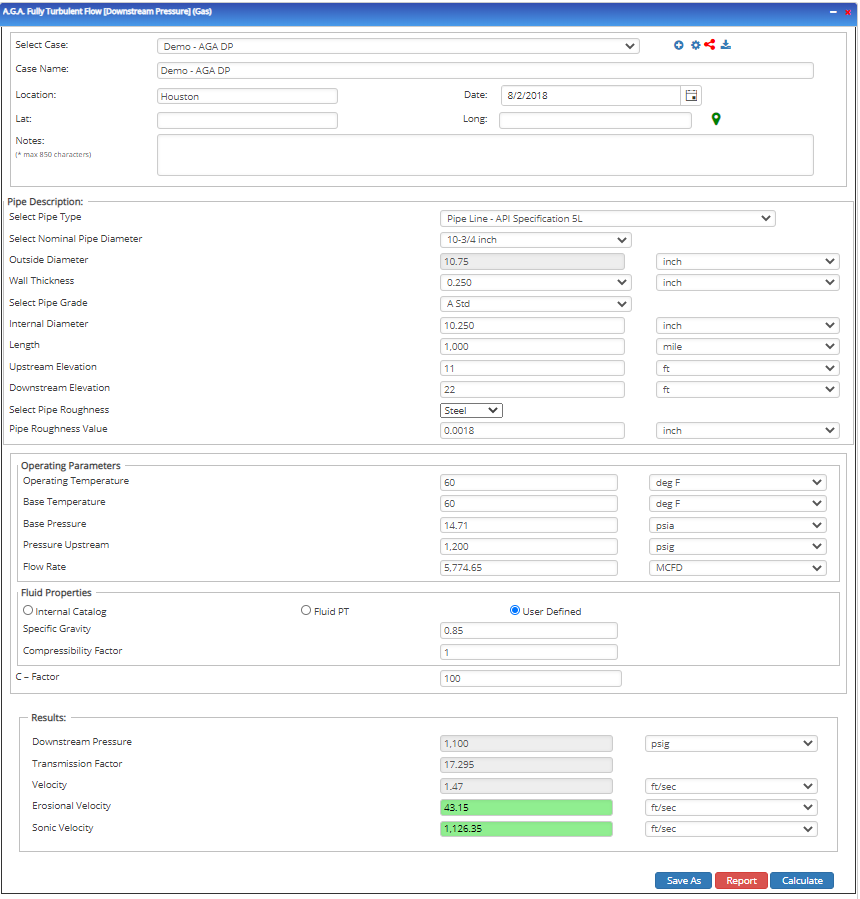
Input Parameters
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Select the Unknown and desired Flow Equation
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date, and any necessary notes
- Fill out all required fields
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units
- Click the CALCULATE button
- Temperature base(°F)
- Pressure base(psia)
- Gas Flowing Temperature(°F)
- Gas Specific Gravity
- Compressibility Factor
- Pipeline Efficiency Factor
- Upstream Pressure(psig)
- Flow Rate(MCFD)
- Internal Pipe Diameter(in)
- Length of Pipeline(mi)
- Upstream Elevation(ft)
- Downstream Elevation(ft)
Outputs/Reports
- View the results
- If an input parameter needs to be edited be sure to hit the CALCULATE button after the change
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel/PowerPoint icon
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
- Flow Rate(ft/sec.)
- Transmission Factor
- Velocity(ft/sec.)
- Upstream Pressure(psi)
- Transmission Factor
- Velocity(ft/sec.)
- Downstream Pressure(psi)
- Transmission Factor
- Velocity(ft/sec.)
- Internal Pipe Diameter(in)
- Transmission Factor
- Velocity(ft/sec.)
- Erosional Velocity
- Sonic Velocity
Flow Rate
Upstream Pressure
Downstream Pressure
Internal Pipe Diameter