Rate of Electrical Current Flow Through the Corrosion Cell
The presence of an electrolyte and a solution between two metals or electrodes is required for galvanic corrosion to occur. Some limitations of the calculation are non-customizable size and type of the electrode and resistivity of the solution.
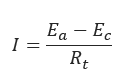
𝐼 − Rate of electrical current flow through the corrosion cell (amps)
𝐸𝑐 − Potential of the cathode with respect to a reference electrode(V)
𝐸𝑎 − Potential of the anode with respect to the same reference electrode,V.
𝑅𝑡 −Total resistance to electrical current dlow through cell(ohms)

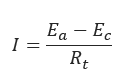
𝐼 − Rate of electrical current flow through the corrosion cell (amps)
𝐸𝑐 − Potential of the cathode with respect to a reference electrode(V)
𝐸𝑎 − Potential of the anode with respect to the same reference electrode,V.
𝑅𝑡 −Total resistance to electrical current dlow through cell(ohms)
Input Parameters
- To create a new case, click the “Add Case” button
- Select the Rate of Electrical Current Flow Through the Corrosion Cell application from the Pipeline Corrosion list.
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required fields.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button.
- Potential of the Cathode with Respect to a Reference Electrode(V)
- Potential of the Anode with Respect to the same Reference Electrode(V)
- Total Resistance to Electrical Current Flow through the Cell(ohm).

Outputs/Reports
- View the results.
- If an input parameter needs to be edited be sure to hit the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel/PowerPoint icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
- Rate of Electrical Current Flow through the Corrosion Cell(A)

