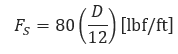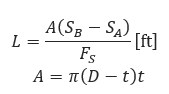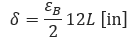Pipe Anchor Force Analysis
The following analysis determines stresses and deflections in pipelines at the transition from below ground (restrained) to above ground (unrestrained) to determine if an anchor is required for above ground pig traps or other piping facilities.
Internal pressure, temperature change, flexibility of to absorb a degree of lateral anchor movement is not considered in this calculation.
Tensile stress due to Poisson effect:
Where:
𝜗 − Poisson′s Ratio = 0.3
𝑃 − Design Pressure(psig)
𝑑 − Inside pipe diameter(in)
𝑡 − Pipe wall thickness(in)
Compressive stress due to temperature change:
Where:
𝐸 − Young′s Mosulus of Elasticity 𝐸=29 x106.
𝛼 − Coefficient of Thermal Expansion for steel α = 6.5 x10−6[in/in℉]
∆𝑇 = 𝑇𝑜 −𝑇𝑖
𝑇𝑜 − Operating Temperature(℉)
𝑇𝑖 − Installation Temperature(℉)
Net longitudinal stress at beginning point (A) of the transition:
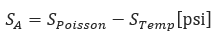
The strain will be 𝜀=0, fully restrained
Net longitudinal stress at end point (B) of the transition: 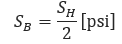
Net strain at point (B), will be: 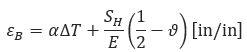
Soil resistance force based on Wilbur’s formula for average soil:
Where:
𝐷 − Outside pipe diameter(in)
Length of transition zone:
Where:
𝐴 − Pipe metal area(in2)
Total pipe movement at point (B) will be:
Anchor force:
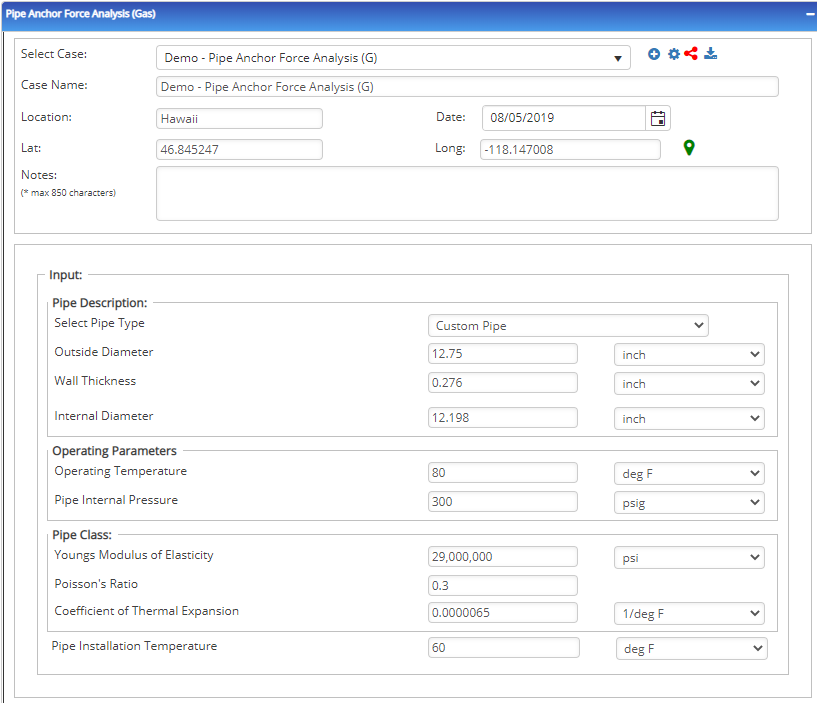
Input Parameters
- Select the Pipe Anchor Force Analysis application from the Steel Pipe – Design and Stress Analysis module.
- To create a new case, click the “+” button
- Enter Case Name, Location, Date and any necessary notes.
- Fill out all required fields.
- Make sure the values you are inputting are in the correct units.
- Click the CALCULATE button.
- Nominal Pipe Size(in):(0.625” – 48”)
- Wall Thickness(in):(0.068”- >2”)
- Pipe grade:(24000psi-80000psi) (if unknown use Grade A 24000)
- Design Pressure(psig)
- Installation Temperature:(-70°F – 160°F)
- Operating Temperature:(-70°F – 160°F)
- Poisson’s Ratio:(0.0 – 0.5)
- Young’s Modulus of Elasticity:(29000000psi – 30000000psi)
- Thermal Expansion Coefficient(1/°F) :(0.0000022in/inF – 0.000012in/inF)
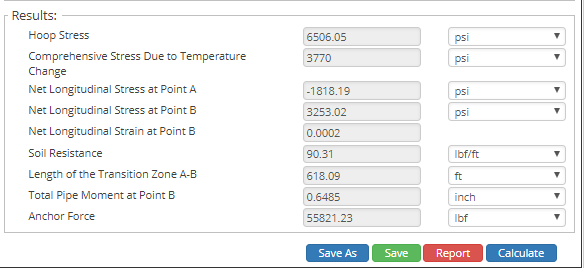
Output Parameters
- View the results.
- If an input parameter needs to be edited be sure to hit the CALCULATE button after the change.
- To SAVE, fill out all required case details then click the SAVE button.
- To rename an existing file, click the SAVE As button. Provide all case info then click SAVE.
- To generate a REPORT, click the REPORT button.
- The user may export the Case/Report by clicking the Export to Excel/PowerPoint icon.
- To delete a case, click the DELETE icon near the top of the widget.
- Hoop Stress(psi)
- Compressive Stress Due to Temperature Change(psi)
- Net Longitudinal Stress at Point A(psi)
- Net Longitudinal Stress at Point B(psi)
- Net Longitudinal Stress at Point B(in/in)
- Soil Resistance(lbf/ft)
- Length of the Transition Zone A-B(ft)
- Total Pipe Moment at Point B(in)
- Anchor Force(lbs.).