Pipe erosion begins when velocity exceeds the value of C/SQRT(ρ) in ft/s, where ρ = gas density (in lb./ft3) and C = empirical constant (in lb./s/ft2) (starting erosional velocity). We used C=100 as API RP 14E (1984). However, this value can be changed based on the internal conditions of the pipeline.
Inputs
Fluid directive is required. Following will be the inputs used which have to be added to the UI
- C – Factor (dimensionless)
- Compressibility Factor (dimensionless)
- Gas Gravity (dimensionless)
- Operating Pressure (psig)
- Operating Temperature (deg F)
Calculation Engine
The following equation will be used for the calculation

Where 100 = “C” and will be user defined (user can change this value to anything)
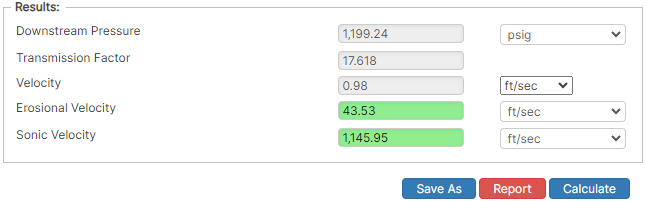
Results
Erosion Velocity in ft/sec
Applicable PLTB Modules & Calculations
- PLTB Hydraulics Liquid
- Colebrook – White
- Darcy – Weisbach
- Darcy – Weisbach Pressure Drop per Mile
- Surge Analysis – Water Hammer
- PLTB Hydraulics Gas
- Panhandle – A
- Panhandle – B
- Weymouth
- A.G.A Fully Turbulent Flow
- Colebrook – White
- FM – Fundamental Equation
- Pipeline Facilities – Gas
- Hot Tap Sizing – Gas
- AGR & GPRA
- Accidental Gas Release Full Bore Pipeline Rupture
- ALR
- Accidental Release from Liquid Hydrocarbon Pipeline
- Pipeline Pumps
- Pump Station Piping – Average Flow Velocity
- Pipeline Compressors
- Compressor Station Piping – Gas Velocity
Example Mockup
If sonic and erosional velocities are under average velocity, the color will be green or grey which indicates no risk
- All units should be left justified – this shows inconsistent justification