Introduction
The Pipeline Toolbox is home to many tools and calculators. The PLTB User’s Guide presents information, guidelines and procedures for use during design, construction, operations and integrity tasks for field or office applications.
When selecting pipe materials, designers, owners and contractors specify materials that provide reliable, long-term service durability, and cost-effectiveness. Solid wall PE pipes provide a cost-effective solution for a wide range of piping applications. PE pipe is also effective for above ground, buried, trenchless, floating and marine installations.
Wheel load from trucks or other vehicles are significant for pipe buried at shallow depths. The resultant load transferred to the pipe depends on vehicle weight, the tire pressure and size, vehicle speed, surface smoothness, pavement and distance from the pipe to the point of loading.
Surcharge loads, such as footings, foundations or other stationary loads, create pressure in the soil beneath the loaded area. This pressure will be distributed through the soil such that there is a reduction in soil pressure acting on the pipe with an increase in depth or horizontal distance from the surcharge area.
Modulus of Soil Reaction (E’) – Values of E’ for Pipe Embedment
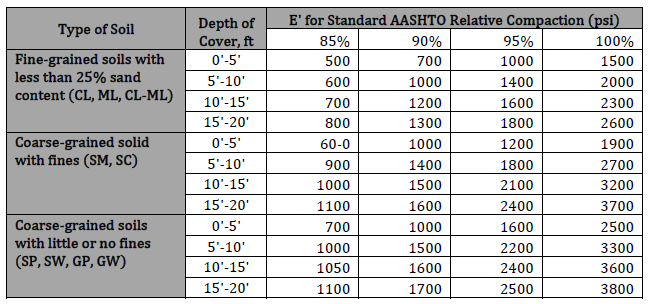
Modulus of Soil Reaction (E’) – Average Values for Iowa Formula
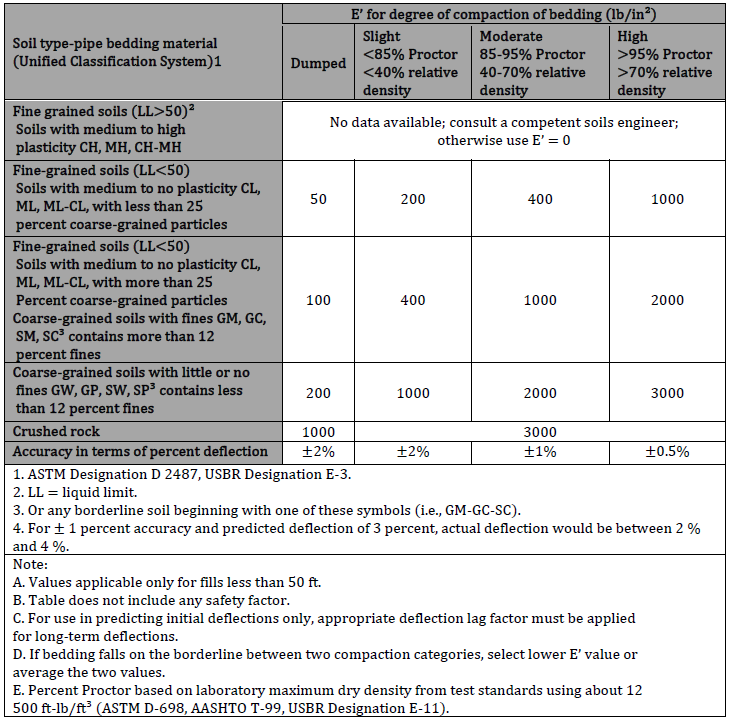
Values of E’n Native Soil Modules of Soil Reaction
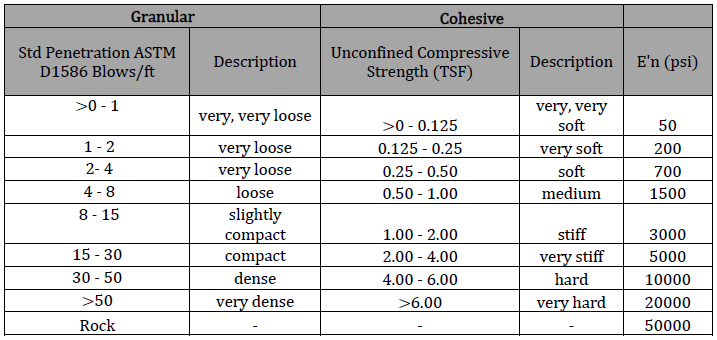
Soil Support Factor
The Soil Support Factor (FS) is a critical parameter in polyethylene (PE) pipe design, as it accounts for the difference in stiffness between the native soil and the embedment soil. The FS value determines how much additional support the native soil provides to the pipe, affecting its deflection and overall stability.
Bd/Do
- Definition: This ratio represents the trench width at the pipe crown divided by the outside diameter of the pipe (Do).
- Significance: The Bd/Do ratio is used to assess the relative size of the trench compared to the pipe diameter. It is an important factor in determining the load distribution and the potential for soil arching effects, which can influence the load-bearing capacity and deflection of the pipe.
E’N/E’
- Definition: This ratio compares the native soil modulus of soil reaction (E’N) to the modulus of soil reaction for the pipe embedment (E’).
- Significance: The E’N/E’ ratio is used to evaluate the relative stiffness of the native soil compared to the embedment material. This comparison helps in understanding how the surrounding soil will interact with the pipe, affecting its deflection and overall stability. A higher ratio indicates that the native soil is stiffer relative to the embedment, which can reduce pipe deflection.
Here is a table that provides typical values for FS based on the ratio of the native soil modulus of soil reaction (E’N) to the modulus of soil reaction for the pipe embedment (E’), and the trench width to pipe diameter ratio (Bd/Do).
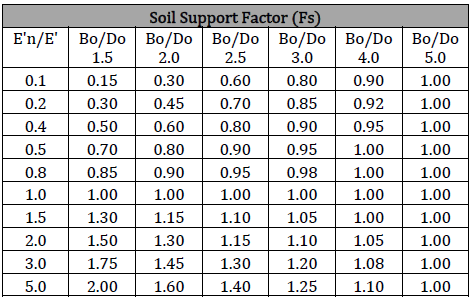
- Higher FS Values (Greater than 1.0): Indicate that the native soil is stiffer than the embedment soil, enhancing the embedment’s resistance to deflection and providing better load distribution.
- Lower FS Values (Less than 1.0): Suggest that the native soil is less stiff than the embedment soil, acting as a reduction factor, meaning less support for the pipe, potentially increasing deflection.
Module/Application
- Design Pressure Polyethylene Pipe
- Wall Thickness Polyethylene Pipe
- Distributed Static Surcharge Load: Directly Beneath a Surcharge Load
- Distributed Static Surcharge Load: Not Directly Beneath a Surcharge Load
- Live Load: Aircraft Load on Buried PE Pipe
- Live Load: AASHTO H20 Load on Buried PE Pipe – 12′ Thick Pavement
- Live Load: AASHTO H20 Load on Buried PE Pipe – Unpaved or Flexible Pavement
- Live Load: Cooper E-80 Railroad Load on Buried PE Pipe
- Live Load: Distributed Surface Load on Buried PE Pipe – Unpaved Road Only
- Live Load: Multiple Wheel Over Buried PE Pipe – Concentrated Point Load
- Live Load: Multiple Wheel Not Over Buried PE Pipe – Concentrated Point Load
- Live Load: Single Wheel Over Buried PE Pipe – Concentrated Point Load
References
- “Modulus of Soil Reaction Values for Buried Flexible Pipe”, Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, ASCE, Vol. 103, No GT 1, Howard, A.K. Technical Toolboxes, Inc.
- “Evaluation of Modulus of Soil Reaction E and its Variation with Depth”, Report No. UCB/GT/82-02,
- “Soil Engineering”, Third Edition, Spangler, M.G. and Handy, R.L., Intext Educational Press
- “Structural Mechanics of Buried Pipes”, Watkins, R.K, and Loren, R, A,
- “Polyethylene Pipe Handbook: Design of PE Piping Systems”, Second Edition, Plastic Pipe Institute, Inc.
- API 15LE – Specification for Polyethylene Line Pipe
FAQ
-
Properties of Polyethylene Pipes?
This property data is a summary of similar materials in the MatWeb database for the category “High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Injection Molded”.
Each property range of values reported is minimum and maximum values of appropriate MatWeb entries. The comments report the average value, and number of data points used to calculate the average.
The values are not necessarily typical of any specific grade, especially less common values and those that can be most affected by additives or processing methods. Check Out
