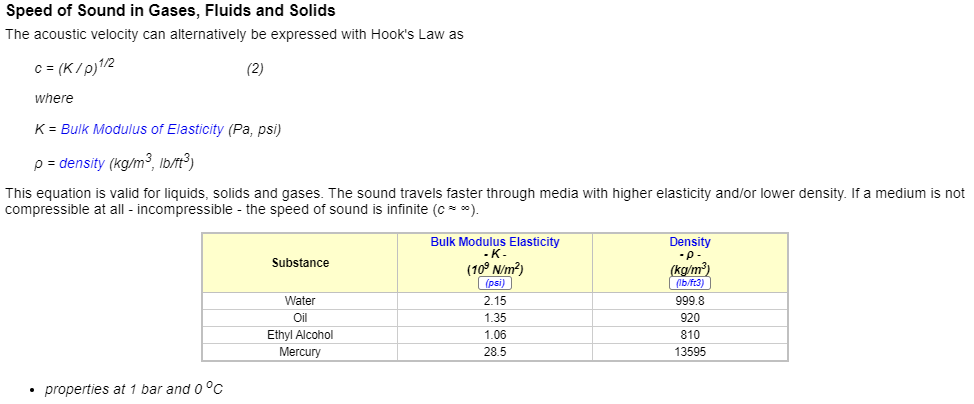
The maximum possible velocity of a compressible fluid in a pipe is called sonic velocity. Oilfield liquids are semi-compressible, due to dissolved gases.
Inputs
Fluid directive is required and following are the input parameters
- K = Cp/Cv – the ratio of specific heats at constant pressure to constant volume (fluid directive)
- G=32.2 ft/sec
- R=1544/mol. Wt.
- T = Absolute temperature in deg R
Calculation Engine
The following equation will be used for the calculation

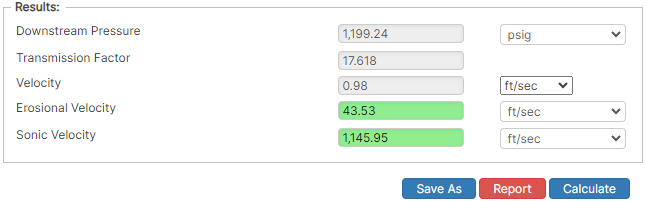
Results
Sonic Velocity in ft/sec
Applicable PLTB Modules & Calculations
- PLTB Hydraulics Liquid
- Colebrook – White
- Darcy – Weisbach
- Darcy – Weisbach Pressure Drop per Mile
- Surge Analysis – Water Hammer
- PLTB Hydraulics Gas
- Panhandle – A
- Panhandle – B
- Weymouth
- A.G.A Fully Turbulent Flow
- Colebrook – White
- FM – Fundamental Equation
- Pipeline Facilities – Gas
- Hot Tap Sizing – Gas
- AGR & GPRA
- Accidental Gas Release Full Bore Pipeline Rupture
- ALR
- Accidental Release from Liquid Hydrocarbon Pipeline
- Pipeline Pumps
- Pump Station Piping – Average Flow Velocity
- Pipeline Compressors
- Compressor Station Piping – Gas Velocity
Example Mockup
If sonic and erosional velocities are under average velocity, the color will be green or grey which indicates no risk
- All units should be left justified – this shows inconsistent justification